- Home
- /
- Product Management
- /
- A Guide to Product Management…
Introduction
Product management is a multifaceted discipline that requires a structured approach to ensure successful product development and delivery. To navigate the complexities of this field, product managers often rely on various Product Management Frameworks and Methodologies. In this article, we will explore several prominent Product Management Frameworks used in product management, each offering unique insights and strategies.
Product Management Frameworks
Customer-Centric Frameworks
These Product Management Frameworks are centered around understanding and meeting customer needs, preferences, and experiences. They help product managers gain insights into user behavior, motivations, and pain points, ultimately guiding product development efforts to create solutions that address real customer problems effectively.
Job To Be Done (JTBD)
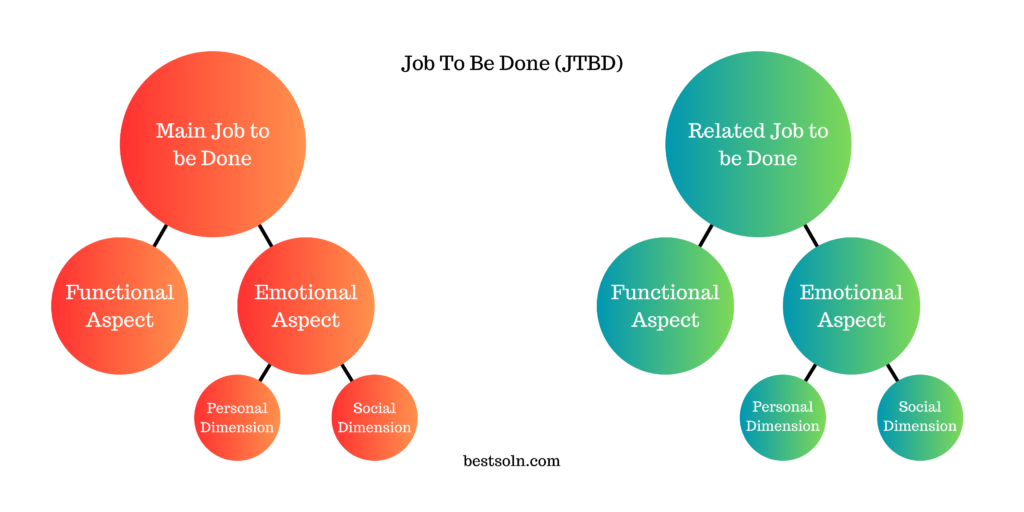
The Job To Be Done framework focuses on understanding the underlying motivations behind why customers hire a product or service. By identifying the “job” customers aim to accomplish, product teams can design solutions that meet their needs effectively. This framework emphasizes customer-centricity and helps uncover unmet needs and opportunities.
Customer Journey Map

A Customer Journey Map provides a visual representation of a customer’s interaction with a product or service across different touchpoints. By empathizing with customers’ experiences and pain points, product teams can identify opportunities for improvement, foster empathy, and optimize the customer journey.
North Star Framework
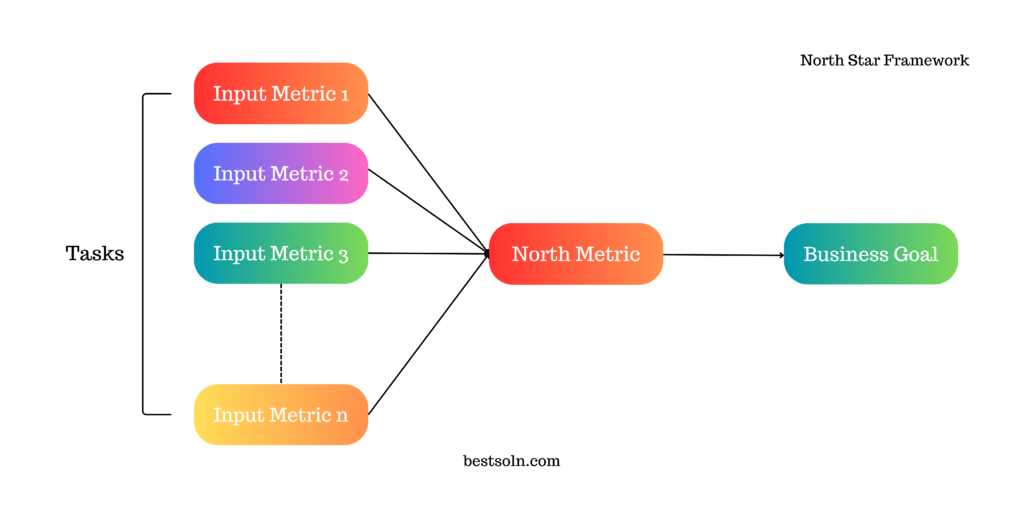
This framework helps establish a single, long-term metric that serves as the guiding light for product development. This metric, often tied to user behavior or business goals, ensures all efforts are aligned toward achieving the ultimate product vision.
Hooked Method

The Hooked Method focuses on creating habit-forming products by incorporating the “Hook Model.” It involves four stages: Trigger, Action, Variable Reward, and Investment. By aligning product experiences with users’ internal triggers and providing variable rewards, this framework aims to build user engagement and retention.
Innovation Adoption Curve
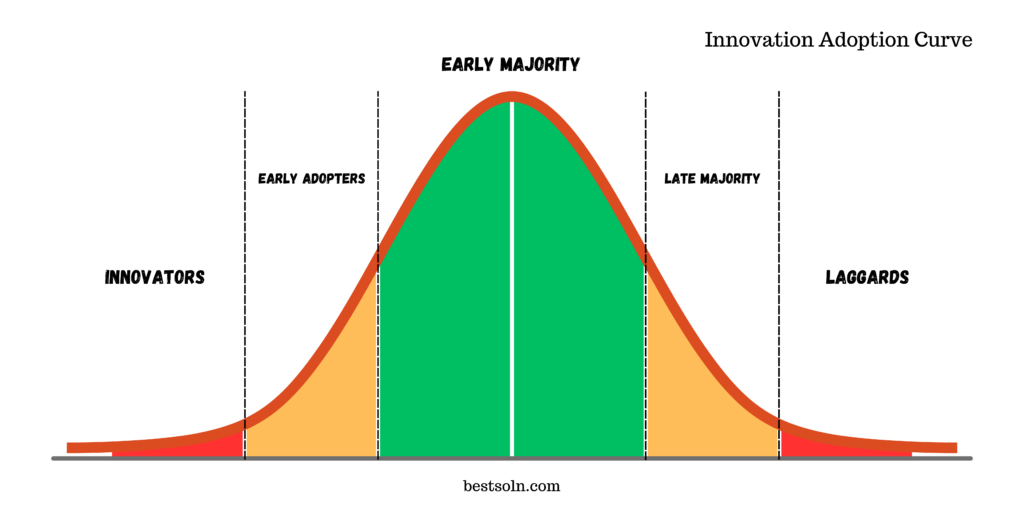
The Innovation Adoption Curve outlines how different segments of the market adopt new products or innovations. By understanding the characteristics and behaviors of Innovators, Early Adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority, and Laggards, product teams can tailor their strategies to effectively reach and engage each segment.
Kano Model
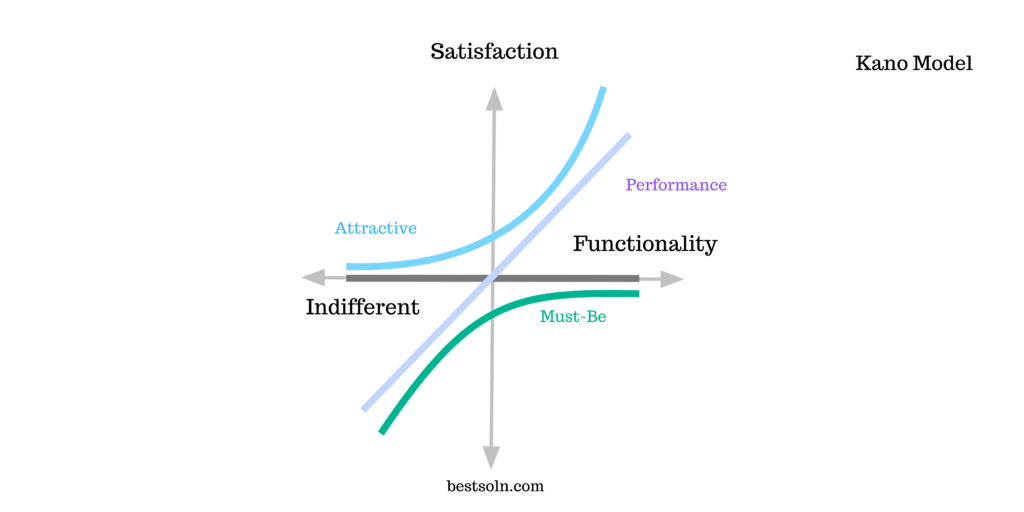
The Kano Model helps product teams understand customer satisfaction by categorizing product features into five categories: Basic, Performance, Excitement, Indifferent, and Reverse. By identifying which features delight customers, this framework guides product development and helps prioritize efforts that drive customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Strategy and Prioritization Frameworks
These Product Management Frameworks focus on strategic planning, prioritization of features or initiatives, and aligning product development efforts with business goals and market opportunities. They assist product managers in defining product strategies, assessing market viability, and making informed decisions about resource allocation and prioritization.
Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
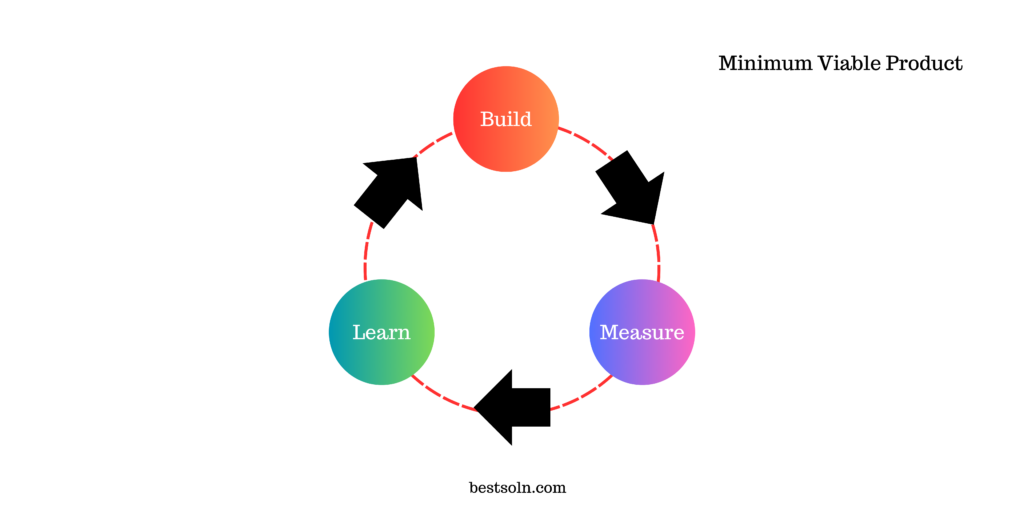
The concept behind MVP is to develop a product with the bare minimum features required to satisfy early customers. By launching an MVP, product teams can gather user feedback, validate assumptions, and iterate quickly, ensuring the development of a market-fit product while minimizing wasted resources.
Working Backwards
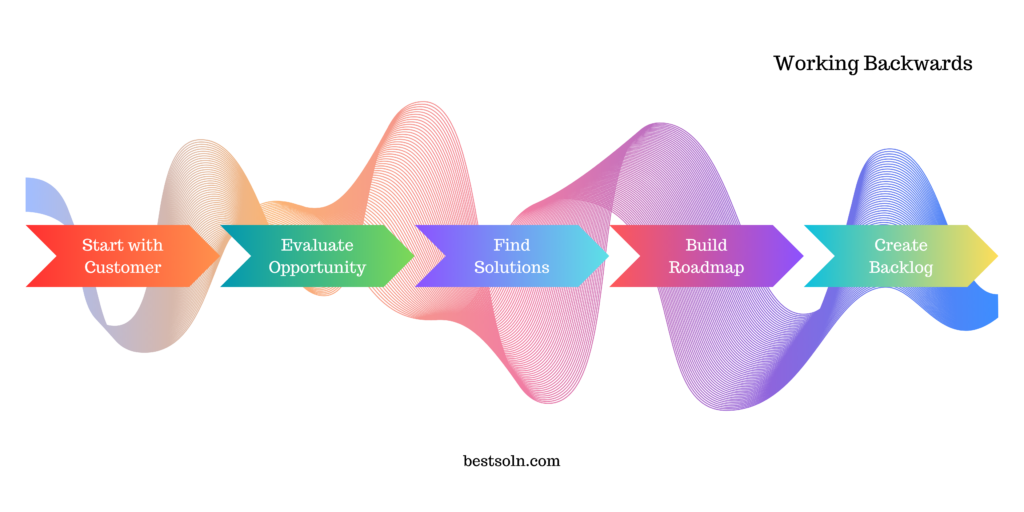
Popularized by Amazon, the Working Backwards framework revolves around envisioning the end-state of a product and working backward to identify essential steps and requirements. By starting with the customer experience and desired outcomes, this framework ensures a customer-centric approach and aligns the team toward a clear vision.
Business Model Canvas
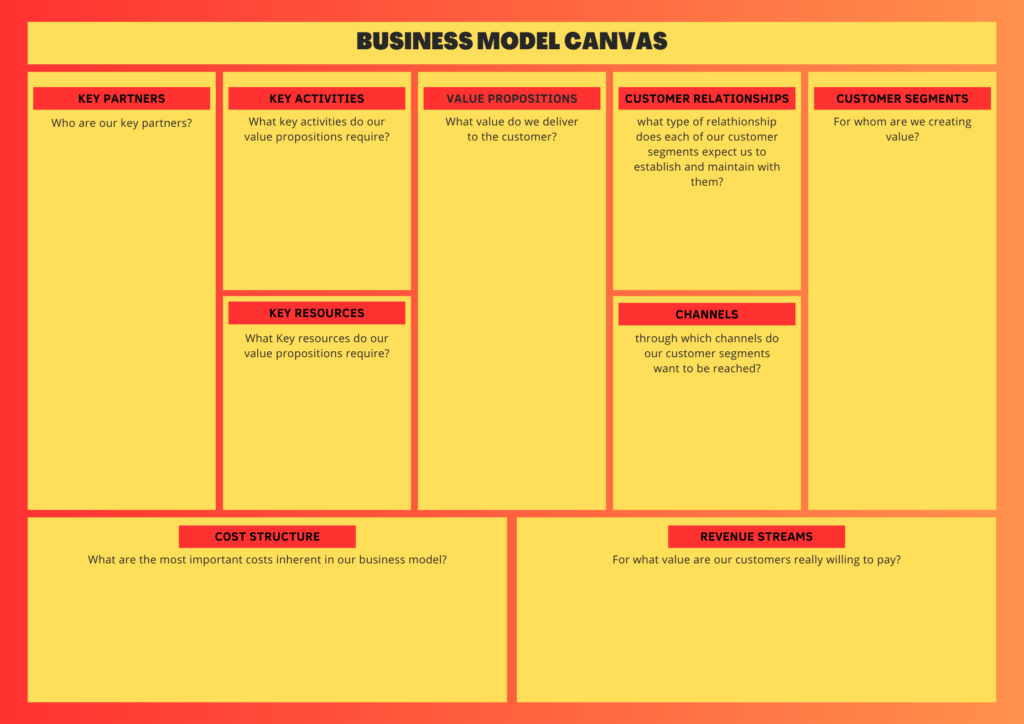
The Business Model Canvas provides a visual representation of how a product or business generates value. It encompasses nine key elements, including Customer Segments, Value Propositions, Channels, Customer Relationships, Revenue Streams, Key Activities, Key Resources, Key Partnerships, and Cost Structure. This framework aids in understanding the overall business model and identifying areas for improvement and innovation.
Opportunity Solution Tree
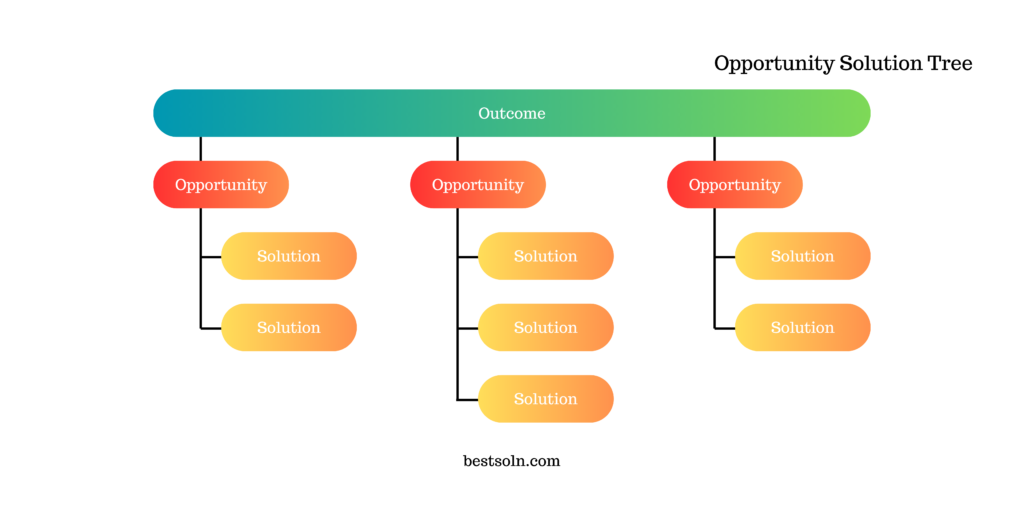
The Opportunity Solution Tree framework is a visual tool that helps product teams explore and prioritize potential solutions for identified customer needs. By mapping out opportunities and potential solutions, product teams can make informed decisions and focus on the most valuable ideas, increasing the chances of success.
Weighted Impact Scoring
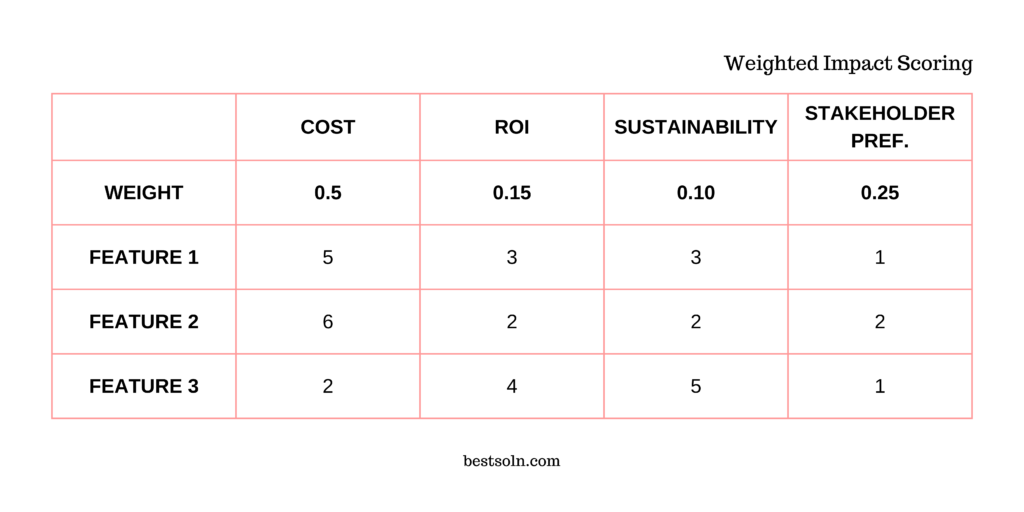
The Weighted Impact Scoring framework enables product teams to prioritize features or projects based on their potential impact and the effort required. By assigning weights to factors like Customer Impact, Market Demand, Technical Complexity, and Business Value, teams can allocate resources wisely and ensure maximum impact with the available resources.
RICE Prioritization
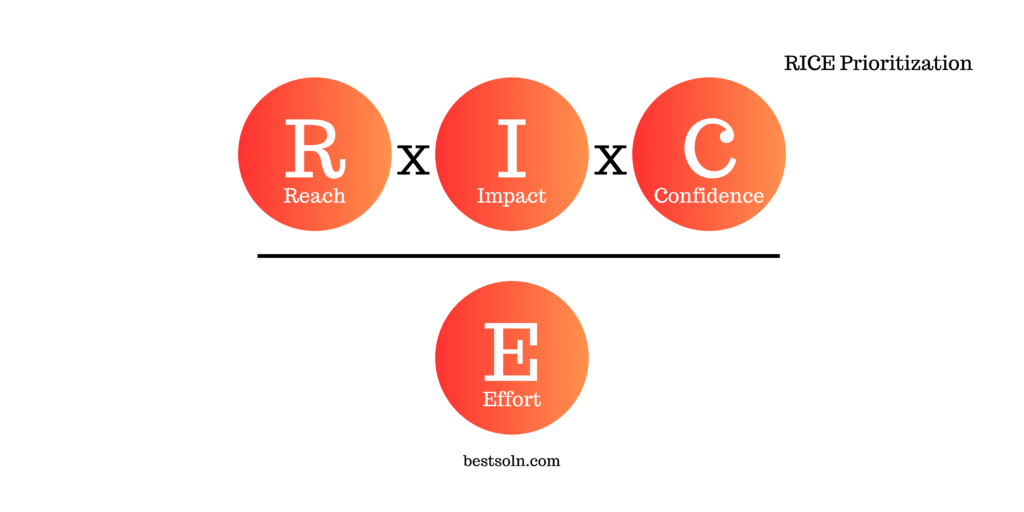
RICE (Reach, Impact, Confidence, Effort) Prioritization is a scoring framework that helps product teams prioritize ideas or initiatives based on their potential impact. By considering four key factors – Reach, Impact, Confidence, and Effort – product teams can prioritize initiatives that are not only impactful but also feasible within their resource constraints.
Product-Market Matrix
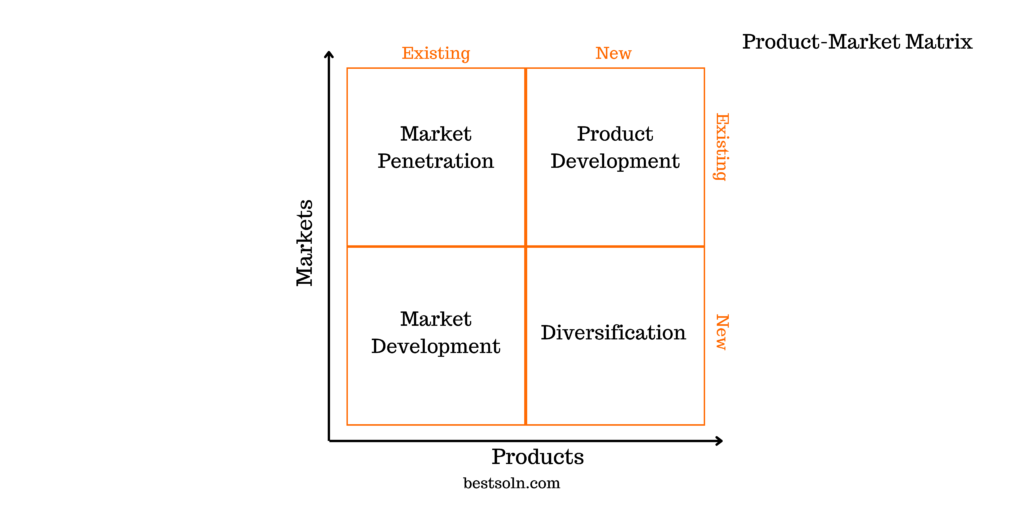
The Product-Market Matrix helps in identifying growth opportunities and making informed decisions about product expansion. By analyzing existing and potential markets and evaluating the fit between products and markets, product teams can identify new target segments, diversify offerings, and maximize market penetration.
Design and Development Frameworks
This category encompasses Product Management Frameworks related to product design, development methodologies, and user experience (UX) design. They emphasize iterative design processes, rapid prototyping, user testing, and agile development practices to create user-centric, innovative, and high-quality products.
Design Sprint

Design Sprint is a time-boxed, structured framework for tackling complex problems and validating solutions through prototyping and user testing. By involving cross-functional teams in a focused sprint, this framework facilitates rapid development, iteration, and validation of potential product solutions.
Double Diamond
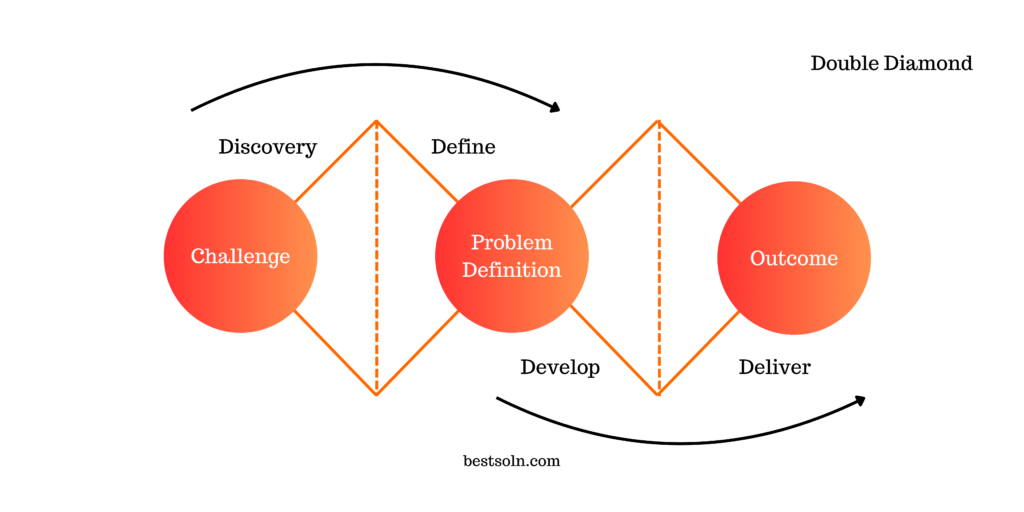
The Double Diamond framework is a visual representation of the divergent (problem space) and convergent (solution space) stages of the design process. It involves four key steps: Discover, Define, Develop, and Deliver. This iterative framework encourages exploration, ideation, validation, and execution, leading to innovative and user-centered product solutions.
Lean Startup Methodology
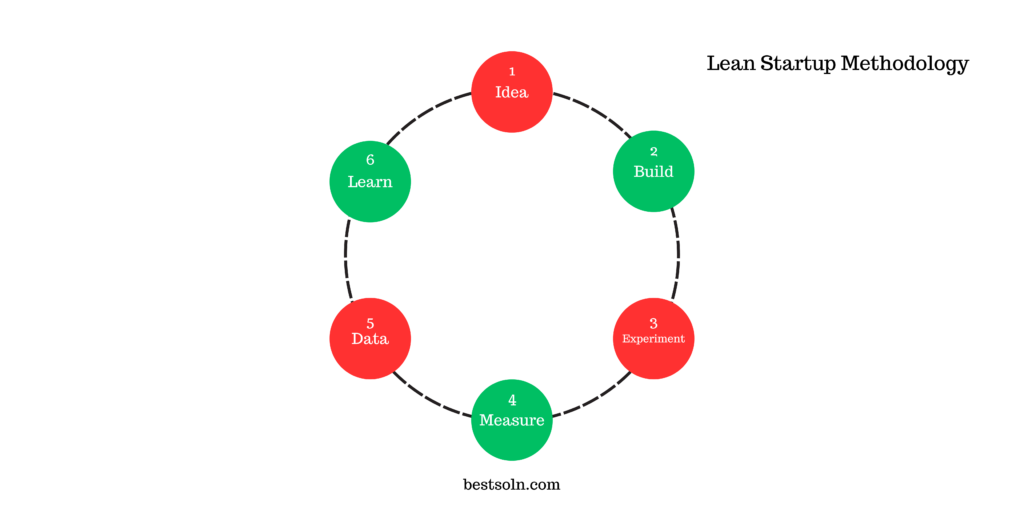
The Lean Startup Methodology, popularized by Eric Ries, emphasizes rapid iteration and learning through validated learning and experimentation. It involves building a minimum viable product (MVP), measuring its performance, and iterating based on customer feedback.
Design Thinking
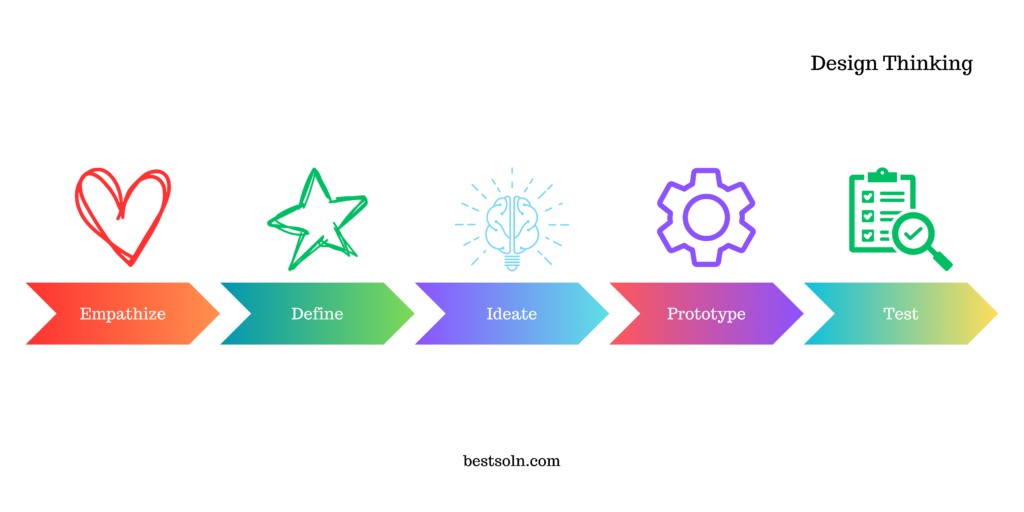
Design Thinking is a human-centered approach to problem-solving that involves empathizing with users, defining the problem, ideating solutions, prototyping, and testing iteratively. It fosters creativity, collaboration, and user-centric innovation.
Agile Development
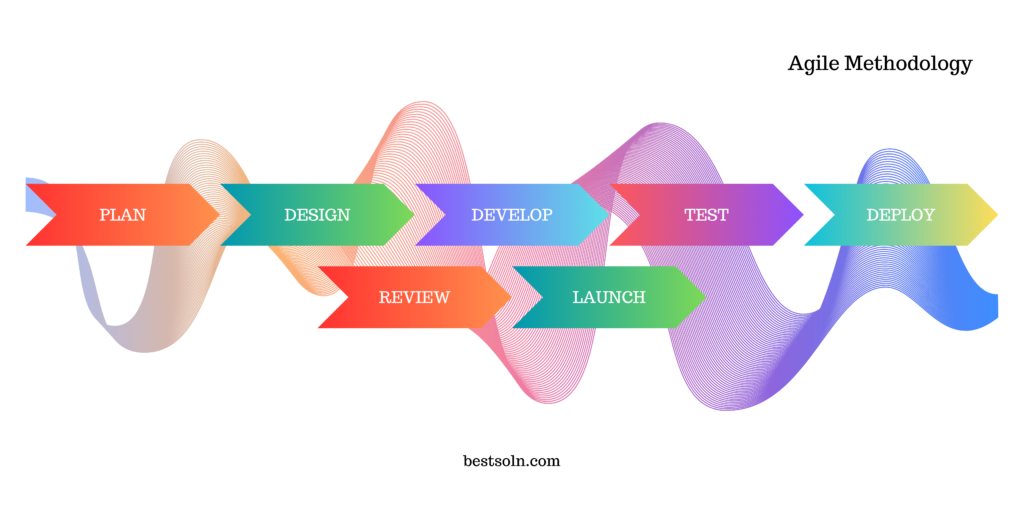
Agile Development is an iterative and incremental approach to software development, emphasizing collaboration, flexibility, and responsiveness to change. It involves breaking projects into small, manageable tasks and delivering working software in short iterations.
Lean UX
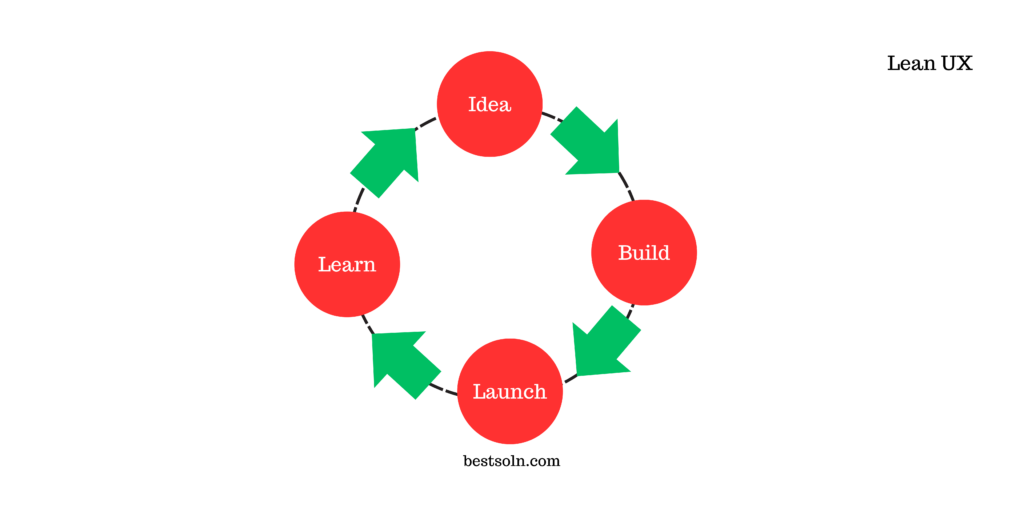
Lean UX combines principles from Lean Startup and Agile methodologies to streamline the user experience (UX) design process. It focuses on rapid prototyping, user testing, and continuous iteration to create user-centric and effective digital products.
Organizational and Decision-Making Frameworks
These Product Management Frameworks are designed to facilitate effective team collaboration, decision-making processes, organizational alignment, and skill development within product management teams. They provide guidelines and structures for managing teams, making strategic decisions, and ensuring efficient execution of product development initiatives.
Spotify Squads

Popularized by Spotify, the Squads framework organizes teams into small, autonomous, multidisciplinary groups (i.e., squads, tribes, chapters, and guilds) that work on specific product areas. This model fosters ownership, collaboration, and rapid decision-making within teams, enabling efficient and effective product development.
DACI (Driver, Approver, Contributor, Informed)
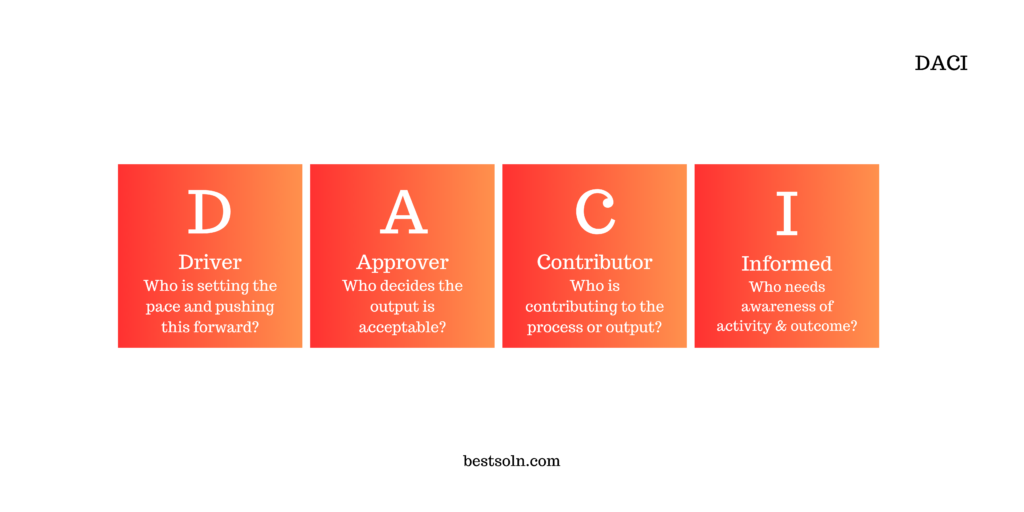
DACI (Driver, Approver, Contributor, Informed) is a decision-making framework that clarifies roles and responsibilities within cross-functional teams. By explicitly defining who is accountable for decisions, who needs to be involved, and who needs to be informed, DACI ensures transparency, accountability, and effective decision-making.
GIST Planning
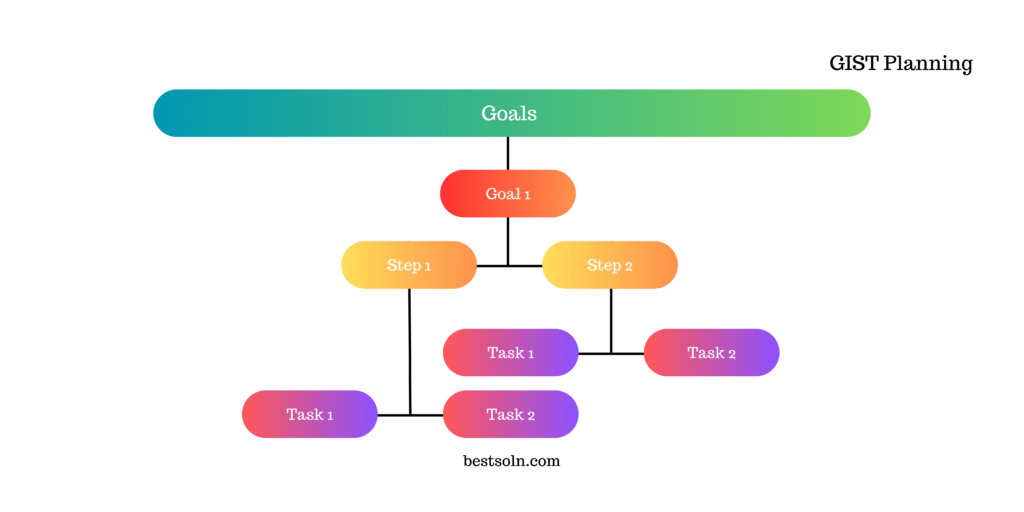
GIST (Goals, Ideas, Steps, Tasks) Planning is a framework that breaks down goals into actionable steps and tasks. By focusing on specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives, GIST Planning ensures clarity, alignment, and effective execution throughout the product development process.
3 Pillars of Product
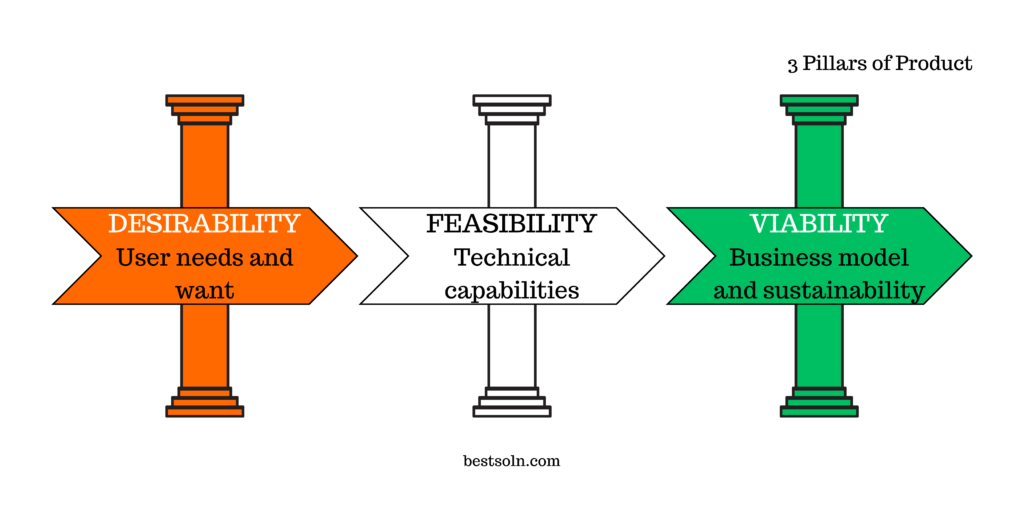
The 3 Pillars of Product framework emphasizes three essential elements – user desirability, technical feasibility, and business viability – that together form the foundation of successful product development. By maintaining a balance between these pillars, product teams can ensure a holistic and sustainable approach to product management.
Product Team Competencies
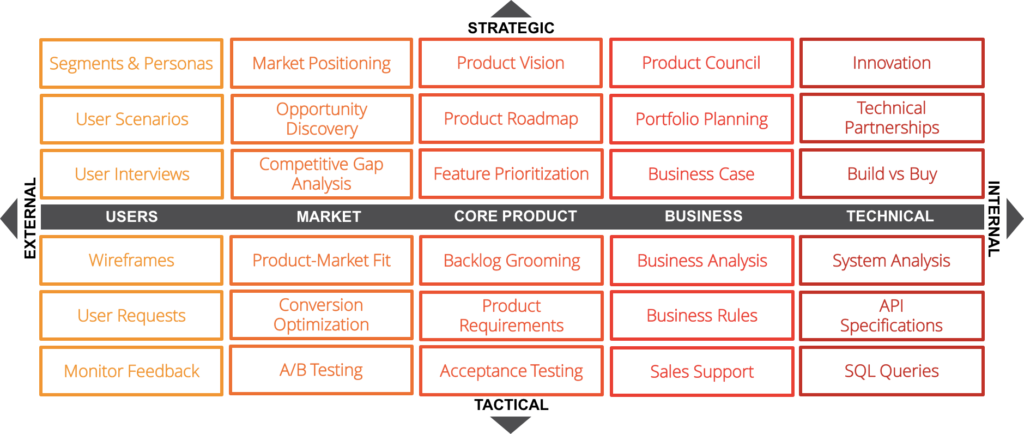
Product Team Competencies framework focuses on defining the necessary skills and competencies required within a product team. It helps identify skill gaps, provides a roadmap for professional development, and fosters a culture of continuous learning and improvement within the team.
Image Source: Neal Cabage
CIRCLES Method
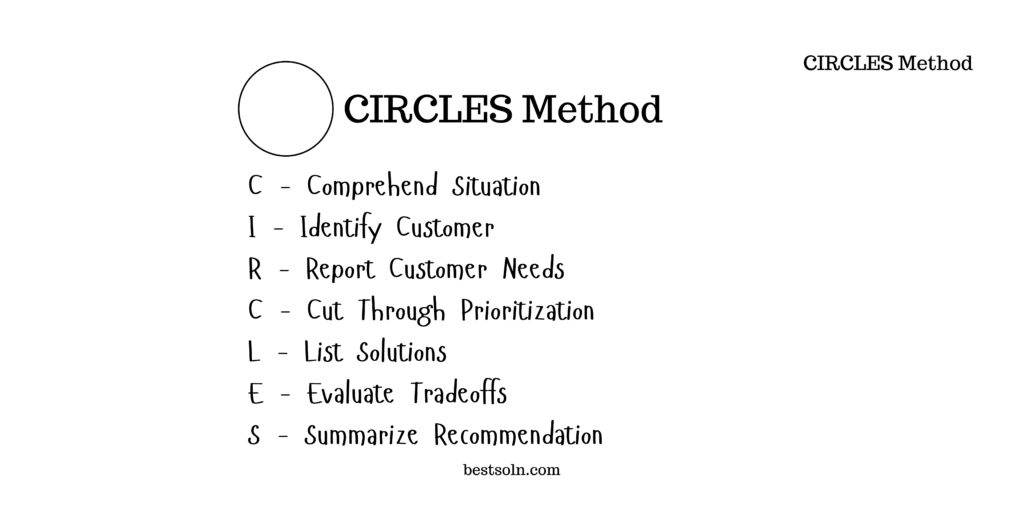
The CIRCLES method is a structured problem-solving framework designed to assist product managers (PMs) in crafting comprehensive and strategic responses to design challenges. This method empowers PMs to approach design questions systematically, ensuring thorough analysis and effective decision-making throughout the product development cycle.
For additional Product Management Frameworks, explore the options available here.
Conclusion
These Product Management Frameworks collectively form a robust toolkit for product managers, enabling them to navigate challenges, prioritize initiatives, and deliver value to customers effectively. By understanding and leveraging these Product Management Frameworks, product managers can drive innovation, foster collaboration, and achieve strategic business goals in today’s dynamic market landscape.



















Leave a Reply