- Home
- /
- Entrepreneurship
- /
- Top 20 Must-know Business Terms…
Introduction
Do you have a killer idea? Are you ready to take on the world with your business? If yes, then hold on! Before you jump into the world of entrepreneurship, there are a few business terms that you should be aware of. Think of these terms as your business toolkit. It will help you understand your business logically, and your numbers, talk to investors confidently, and navigate the business jargon. Understanding these business terms can be a game-changer for your entrepreneurial journey and significantly improve your decision-making process. This blog aims to provide you with a thorough list of the top 10 must-know business terms compiled by us that every entrepreneur should know. Before we go over the list, we would like to state that our list’s logical order starts from understanding the market and customer base, defining value propositions and business models, managing finances and operations, tracking performance metrics, and planning for future growth and transitions. So, let’s dive in!
Market Segmentation

One size doesn’t fit all in business; therefore, we need to understand market segmentation. Market segmentation helps you divide your target market into smaller and more manageable groups based on similar characteristics and preferences such as demographics, behavior, and needs. This way, you can tailor your products or services and marketing strategy to specific groups more effectively. With more focus, a better product or service can be built that can help in building a consistent revenue stream.
Example
A skincare company segments its market based on age groups such as acne products for teenagers, anti-aging for older adults, and general skin care for young adults.
Value Proposition

Value proposition defines the unique value your product or service offers to customers. It’s that core proposition that sets your business apart from the competition. It communicates in customers’ minds why they should choose you over others and what benefits they can expect. As an entrepreneur, one should develop a compelling value proposition that sets you apart from competitors and helps you in marketing, sales, and overall brand positioning.
Example
Amazon’s Value Proposition is Amazon’s promise of fast and convenient delivery, a wide selection of products, and competitive pricing, providing customers with a seamless online shopping experience and value for their money.
Target Market

After segmenting the market, the next logical step would be choosing your target market. The target market refers to the specific group of people you are trying to reach with your product or service. Think of them as your ideal customers who are most likely to be interested in and purchase your products or services.
Example
The target market for a fitness apparel brand specializing in activewear for women is active millennial women aged 25-35 with a health-conscious and active lifestyle. These women are more aware of their choices, style, function, and comfort. They value brands that align with their values of inclusivity, empowerment, and sustainability, making them ideal customers for a brand that offers eco-friendly options and inclusive sizing.
Unique Selling Proposition (USP)

A unique Selling Proposition (USP) is what makes your business special. It’s the core feature of your product that can convince someone to choose your product or service over the competition. Your USP is your secret weapon, which sets you apart and makes you desirable to your target customer.
Example
Apple’s “Think Different” campaign, emphasized innovation, creativity, and unique design in their products, setting Apple apart from competitors and appealing to customers looking for cutting-edge technology with a focus on user experience.
Marketing Funnel
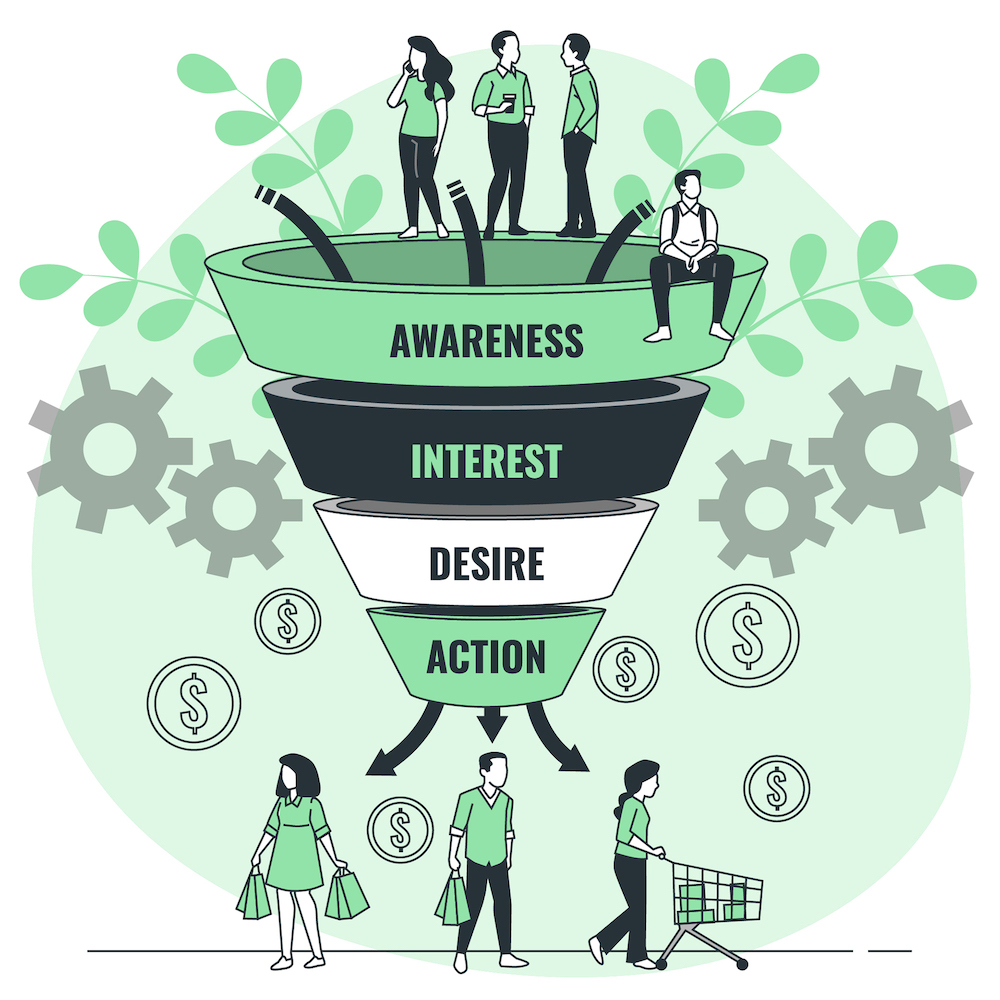
A marketing funnel represents the journey of your potential customers from awareness to purchase. Usually, it’s represented using the AIDA model i.e., Awareness, Interest, Consideration, Decision, and Retention. It helps you visualize how you can attract leads, nurture their interest, and convert them into paying customers.
Example
A marketing funnel example involves a software company promoting a productivity app:
1. Awareness: Social media ads introduce the app’s benefits.
2. Interest: Website visitors download a free trial.
3. Consideration: Email campaigns highlight features.
4. Decision: Users purchase or subscribe.
5. Retention: Ongoing support maintains user loyalty.
Business Model

A business model is the roadmap to a start-up’s success. It outlines how a business will create value, deliver products or services to customers, and make money. Having a well-planned business model helps in staying focused and making strategic decisions.
Example
An example of a business model is a subscription-based streaming service like Netflix. The company offers a wide range of movies, TV shows, and original content to subscribers for a monthly fee. By providing unlimited access to a vast library of entertainment content, Netflix generates revenue through subscription fees rather than individual purchases. This business model allows Netflix to attract a large customer base, retain subscribers through continuous content updates, and scale its operations globally.
Return on Investment (ROI)

Return on investment (ROI) is a fundamental concept in business that measures the profitability of an investment relative to its cost. As an entrepreneur, understanding ROI helps in evaluating the potential success of a business by making informed decisions about where to allocate resources for maximum returns.
Example
A company invests $10,000 in a marketing campaign and generates $50,000 in additional revenue directly attributed to that campaign. The ROI for this investment would be 400% i.e., for every dollar invested in the marketing campaign, the company earned $4 in profit.
Profit vs. Revenue

Revenue is the total amount of money you make from selling your product or service. Profit, on the other hand, is what’s left after you subtract all your expenses from your revenue. Profitability is calculated by dividing net profit by revenue and is expressed as a percentage. Understanding profit margin helps price offerings competitively and optimize the business’s financial performance.
Example
A bakery generates $10,000 in revenue and incurs $6,000 in expenses, resulting in a net profit of $4,000. The profit margin, calculated as (Net Profit / Revenue) * 100, is 40%. This indicates that the bakery retains 40 cents in profit for every dollar of revenue generated, helping it price competitively and manage financial performance efficiently.
Cash Flow

Cash flow refers to the movement of money in and out of a company. Entrepreneurs must manage and monitor cash flow effectively to sustain business operations, pay bills, and invest in growth opportunities. Adequate cash flow management ensures a healthy financial outlook for a venture. In short, understanding cash flow helps in managing expenses, planning for growth, and ensuring financial stability.
Example
Here’s a shorter example of cash flow for a small retail business:
Inflows
- Sales revenue: $20,000
- Loans/investments: $5,000
Outflows
- Cost of goods sold: $10,000
- Operating expenses: $8,000
- Loan repayments: $2,000
Cash Flow = ($20,000 + $5,000) – ($10,000 + $8,000 + $2,000) = $5,000 (positive cash flow)
This positive cash flow of $5,000 means the business has more money coming in than going out, supporting expenses, investments, and financial stability.
Break-Even Point

The break-even point is one of the important business terms that measure the time to business viability, i.e., it tells when a business’s total revenue equals total expenses, resulting in neither profit nor loss. Knowing the break-even point helps set pricing strategies, plan for growth, and assess the financial health of a business.
Example
Here’s a shorter example:
Fixed Costs
- Rent: $3,000
- Salaries: $2,000
- Equipment lease: $1,000
- Total Fixed Costs: $6,000
Variable Costs per unit: $18 Selling Price per unit: $25
Break-Even Quantity = $6,000 / ($25 – $18) = 857 units
The break-even point for this manufacturing business is 857 units, meaning they need to sell at least this many units to cover all costs and avoid losses.
Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization (EBITDA)
EBITDA stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization. It is a financial metric used to assess a company’s operating performance and profitability by excluding non-operating expenses such as interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. EBITDA provides a clearer picture of a company’s core earnings from its primary business activities and is often used by investors, analysts, and creditors to evaluate a company’s financial health and compare its performance across different industries.
Example
Let’s simplify the example:
XYZ Corp’s revenue: $1,000,000
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) + Operating Expenses: $700,000
Depreciation: $50,000
Interest Expense + Taxes: $40,000
EBITDA = Revenue − (COGS + Operating Expenses) + Depreciation
EBITDA = $1,000,000 − $700,000 + $50,000 = $350,000
So, XYZ Corp’s EBITDA is $350,000 for that period.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)

KPIs are one of the important business terms that demonstrate how effectively a company is achieving its key business objectives. Identifying and monitoring the right KPIs enables tracking progress, measuring success, and improving strategies accordingly. Some of the common examples of KPIs include revenue growth, customer acquisition, and customer satisfaction.
Example
Here are shorter examples of KPIs across different areas:
- Sales
- Sales Revenue
- Conversion Rate
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
- Marketing
- Website Traffic
- Lead Conversion Rate
- Return on Advertising Spend (ROAS)
- Finance
- Gross Profit Margin
- Operating Income
- Cash Flow
- Customer Service
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
- First Response Time
- Human Resources
- Employee Turnover Rate
- Employee Satisfaction Index
- Time to Hire
These KPIs are vital for measuring performance and making informed decisions across various business functions.
Networking

Networking is about building genuine relationships with other professionals who can offer support, advice, and opportunities. Cultivating a strong network can open doors and accelerate your business growth.
Example
John, a software engineer, attends tech conferences, connects with professionals, shares expertise, and follows up for potential collaborations and career growth.
Supply Chain Management

Supply chain management involves the coordination and optimization of all activities involved in the production, procurement, and distribution of goods or services. A solid understanding of supply chain management helps entrepreneurs streamline operations, reduce costs, and ensure the timely delivery of products or services to customers.
Example
In a retail company selling clothing:
1. Supplier Relations: Source materials like fabric.
2. Production: Manufacture clothing based on demand.
3. Distribution: Send products to warehouses for store delivery.
4. Retail Stores: Display and sell clothing to customers.
5. Inventory Management: Optimize stock levels to meet demand.
6. Logistics: Efficiently transport products to stores and customers.
7. Returns: Handle returns and manage reverse logistics.
Effective supply chain management ensures smooth operations, cost efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
Scalability

Scalability refers to the ability to handle the increase in customers or production without falling apart. As a business grows, scaling becomes essential. It involves increasing operations, production, and customer base while maintaining efficiency and profitability. Knowing how to scale effectively is key to long-term success.
Example
A SaaS company starts with 100 customers for its project management tool. As it grows, scaling becomes crucial to handle increasing users efficiently. By investing in scalable infrastructure and optimizing software performance, the company can seamlessly accommodate growth and maintain a positive user experience, ensuring long-term success.
Intellectual Property

Intellectual property refers to any creations of the mind that have commercial value, such as inventions, literary or artistic works, designs, or symbols. Protecting your intellectual property is crucial for entrepreneurs as it safeguards the uniqueness and value of your ideas, innovations, and brand.
Example
A pharmaceutical company’s patent for a new drug formula. This patent protects the company’s innovative research and development efforts, granting them exclusive rights to manufacture and sell the drug for a specified period. This intellectual property ensures that competitors cannot replicate the formula without permission, allowing the company to recoup its investment and maintain a competitive advantage in the market.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)

Customer Acquisition Cost refers to how much it costs your business to acquire a new customer. Calculating CAC helps us understand the efficiency of your marketing and sales efforts and calibrate your customer acquisition strategies.
Example
A digital marketing agency spends $1,00 on advertising campaigns across social media. During the campaign, they acquired 100 new customers. To calculate CAC, we will divide the total marketing spending i.e., $1,000 by the number of customers acquired i.e., 100 in our case. Hence, the CAC per customer would be $10 per customer. This means the agency spent $10 on average to acquire each new customer through marketing efforts.
Burn Rate

Burn rate tells us the rate at which a company is spending its available capital over a specific period. Monitoring the burn rate helps a company manage cash flows effectively so that the company can optimize its budget according to the current reality and sustain financial health.
Example
A startup spends $50,000 monthly on expenses. With $500,000 in reserves, its burn rate shows it can sustain for 10 months without new revenue. Tracking burn rate aids in financial planning and decision-making.
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats Analysis (SWOT)

SWOT analysis is a strategic self-assessment for a business. It helps in assessing a company’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. This analysis helps entrepreneurs identify internal and external factors that may impact their business. By understanding their strengths and weaknesses and capitalizing on opportunities while managing threats, entrepreneurs can make well-informed decisions and develop successful strategies.
Example
SWOT analysis of a marketing agency:
1. Strengths: Highly skilled team
2. Weaknesses: Limited marketing budget
3. Opportunities: Growing demand for digital marketing
4. Threats: Increasing competition
This analysis guides strategy development to leverage strengths, address weaknesses, capitalize on opportunities, and mitigate threats.
Exit Strategy

An exit strategy outlines how an entrepreneur plans to exit a business venture while maximizing potential returns. Having a clear exit strategy in place from the start can help you navigate future transitions, attract investors, and ensure long-term success.
Example
A tech startup plans to be acquired within five years. They focus on building value through product development and revenue growth. Once reaching milestones, they negotiate a sale, allowing founders and investors to realize returns and pursue new ventures.
Conclusion
As an entrepreneur, mastering these top twenty business terms will equip you with essential knowledge and understanding that will make you a master in navigating through the challenges and opportunities that come your way. By understanding these business terms well, you can confidently make informed decisions, plan your strategies efficiently, and communicate your ideas to stakeholders effectively. These top twenty business terms are just the tip of the iceberg; therefore, continuous learning and staying updated on industry-specific terminologies will set you on the path to entrepreneurial excellence. Also, check out our business glossary to learn more business terms for your entrepreneurial success.




















Leave a Reply